
29 Sep How Is Cardiac Muscle Tissue Different from Other Muscle Tissues?
What is cardiac muscle?
Cardiac muscle tissue is just one of the 3 different types of muscle tissue in your body. The other two forms are skeletal muscle tissue and smooth muscle tissues. Cardiac muscle tissue is simply found in your heart, where it performs coordinated contractions that allow your heart to pump blood through your circulatory system.
Keep reading to learn more about the function and arrangement of cardiac muscle tissue, in addition to conditions that affect this type of muscle tissue.
How does this function?
Cardiac muscle tissue works to keep your heart pumping through involuntary movements. This is 1 feature that distinguishes it from skeletal muscle tissue, which you can control.
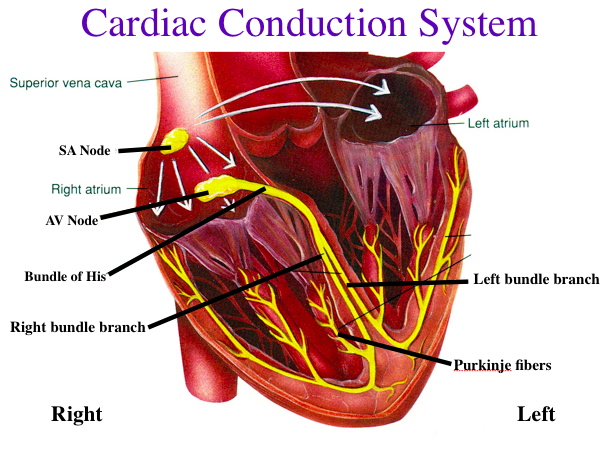
It does this through specialized cells called pacemaker cells. These control the contractions of your heart. Your nervous system sends signals to pacemaker cells which prompt them to speed up or slow down your heart rate.
Your pacemaker cells are linked to additional cardiac muscle cells, letting them pass along signs. This results in a wave of contractions of your cardiac muscle, which generates your heartbeat. Find out more about how your heart works.
What exactly does cardiac muscle tissue look like when it moves?
Use this interactive 3-D diagram to learn more about the movement of cardiac muscle tissue.
Which are core muscles made of?
Intercalated discs
Intercalated discs are little connections that join cardiac muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) to every other.
Gap junctions
Gap junctions are a part of their intercalated discs. When one cardiac muscle is stimulated to contract, then a gap junction transfers the stimulation to the upcoming cardiac cell. This permits the muscle to contract in a coordinated way.
Desmosomes
Like gap junctions, desmosomes can also be found within intercalated discs. They help maintain the cardiac muscle fibers together through a contraction.
Nucleus
The nucleus is the”control center” of a cell. It includes all the cell’s genetic material. While skeletal muscle cells can have multiple nuclei, cardiac muscle cells typically only have one nucleus.
What’s cardiomyopathy?
Cardiomyopathy is one of the chief conditions that can affect your cardiac muscle tissue. It’s a disorder that makes it harder for the heart to pump blood.
There are Many Different Kinds of cardiomyopathy:
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. The cardiac muscles expand and thicken for no clear reason. It is usually found at the lower chambers of the heart, called the ventricles.
- Dilated cardiomyopathy. The ventricles become bigger and poorer. This makes it hard for them to pump, making the rest of your heart work harder to pump blood.
- Restrictive cardiomyopathy. The ventricles become rigid, which prevents them from filling to their full volume.
- Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia. The cardiac muscle tissue of the right ventricle is replaced with fatty or polyunsaturated tissue. This can lead to arrhythmia, which refers to an abnormal heart rate or rhythm.
Not all instances of cardiomyopathy create symptoms. But it can sometimes lead to:
- Trouble breathing, particularly when exercising
- Fatigue
- Swollen ankles, feet, legs, stomach, or neck veins
It is usually difficult to pinpoint the cause of cardiomyopathy. But several things can increase your risk of developing it, such as:
- A family history of cardiomyopathy or heart failure
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
- Heavy alcohol ingestion
- Use of recreational drugs
- Past heart attacks or heart ailments
How does exercise affect cardiac muscle tissue?
Much like many other muscles in your body, exercise may strengthen your stomach muscle. Exercise can also help lower your risk of developing cardiomyopathy and make your heart work more efficiently.
The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise each week. To reach this aim, attempt to have about 30 minutes of exercise five days a week.
As for the type of exercise, cardio workouts are named for their cardiac muscle benefits. Regular cardio exercise might help lower your blood pressure, lower your pulse, and make your heart pump more efficiently. Frequent kinds of cardio exercises include walking, running, biking, and swimming pool.
If you currently have heart disease, be sure that you talk to your physician before starting any sort of exercise program. You might have to take some precautions to avoid placing too much strain on your heart. Learn about the different signs of heart problems while exercising.
The bottom line
Cardiac muscle tissue is one of the 3 different types of muscle on your body. It is only found on your heart, where it’s involved with coordinated contractions that help keep your heart beating. To keep your cardiac muscle functioning effectively and to decrease your risk of cardiac conditions — such as cardiomyopathy — try to get into some kind of exercise more days of the week than not.


Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.